In modern software development, data formats play a critical role in how applications store, exchange, and manage information. Two popular formats that often come up are JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) and TOML (Tom’s Obvious, Minimal Language).
While both look similar at first glance, they serve different purposes and shine in different scenarios. In this article, we’ll explore what JSON is, what TOML is, why both exist, their real-world use cases, and the key differences between JSON and TOML — all in a simple, practical way.
Overview
JSON and TOML are lightweight, human-readable data formats used to structure information.
- JSON is primarily designed for data exchange between systems, especially APIs and web services.
- TOML is designed for configuration files, making them easier for humans to read, write, and maintain.
Understanding when to use JSON vs TOML can help you build cleaner systems, reduce errors, and improve maintainability.
What is JSON?
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a text-based data format used to represent structured data. It is language-independent and supported by almost every programming language and platform.
JSON is commonly used in:
- REST APIs
- Microservices communication
- Frontend–backend data exchange
- Cloud services and SaaS platforms
Example:
{
"name": "TechBytechies",
"type": "blog",
"active": true,
"visitors": 12000
}
Why JSON is popular
- Extremely lightweight and fast
- Easy to parse by machines
- Supported natively in JavaScript and widely across all ecosystems
- Ideal for transmitting data over the network
What is TOML?
TOML (Tom’s Obvious, Minimal Language) is a configuration file format designed to be easy for humans to read and edit, while still being easy for machines to parse.
It is commonly used in:
- Application configuration files
- Infrastructure and DevOps tooling
- Package managers and build tools
Example:
title = "TechBytechies"
active = true
visitors = 12000
Why TOML exists
TOML was created because formats like JSON and YAML were either too strict, too complex, or too error-prone for configuration use. TOML focuses on:
- Clear syntax
- Strong typing
- Predictable behavior
- Minimal ambiguity
Why Do We Need Both JSON and TOML?
JSON and TOML solve different problems:
| Need | Best Format |
|---|---|
| Machine-to-machine communication | JSON |
| API responses and requests | JSON |
| Human-editable configuration files | TOML |
| Clear, typed configuration | TOML |
| Network data transmission | JSON |
| Application settings | TOML |
In short:
- JSON is optimized for machines.
- TOML is optimized for humans.
That’s why both formats continue to exist and thrive.
Use Cases
JSON Use Cases
- REST and GraphQL APIs
- Frontend–backend communication
- Event streaming (Kafka, Pub/Sub)
- Data storage in NoSQL databases
- Web and mobile applications
TOML Use Cases
- Application config files (
config.toml) - DevOps tools (Terraform, Hugo, Rust projects)
- Environment and deployment settings
- Tooling and package manager configuration
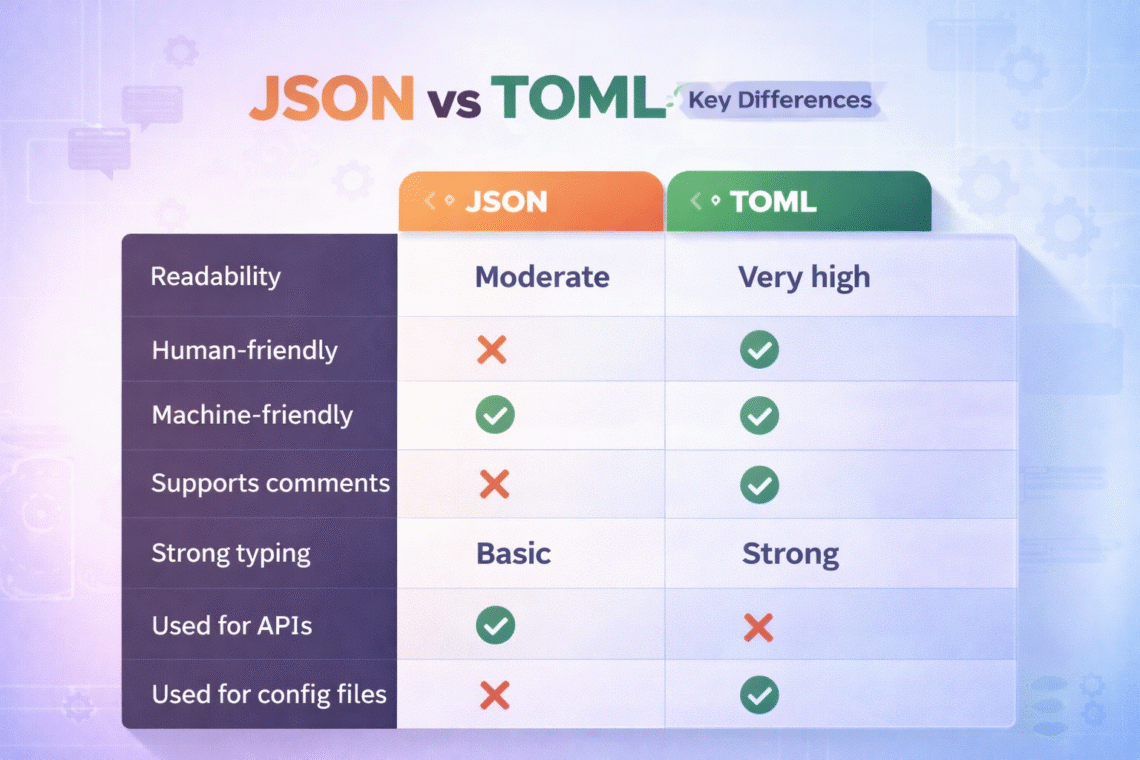
JSON vs TOML: Key Differences
| Feature | JSON | TOML |
|---|---|---|
| Readability | Moderate | Very high |
| Human-friendly | ❌ | ✅ |
| Machine-friendly | ✅ | ✅ |
| Supports comments | ❌ | ✅ |
| Strong typing | Basic | Strong |
| Used for APIs | ✅ | ❌ |
| Used for config files | Sometimes | ✅ |
| Error-prone for humans | Yes (strict syntax) | Less |
| Trailing commas allowed | ❌ | Depends on parser |
Final Thoughts
Choosing between JSON and TOML isn’t about which is better — it’s about which is right for your use case.
- Use JSON when your system needs fast, efficient, and standardized data exchange.
- Use TOML when you want clean, readable, and maintainable configuration files.
Both formats are essential in modern software architecture, and understanding their strengths helps you design better systems.