Overview
Generative AI has made huge progress, but even the most advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) still face a major challenge: they don’t have access to real-time or private data. This often leads to outdated answers or AI hallucinations.
This is where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) plays a critical role.
RAG is a modern AI architecture that enhances LLMs by connecting them with external knowledge sources such as documents, databases, and websites. Instead of guessing, the AI retrieves relevant information first and then generates accurate, context-aware responses.
Today, RAG is becoming the backbone of enterprise AI, RAG chatbots, and document Q&A systems.
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
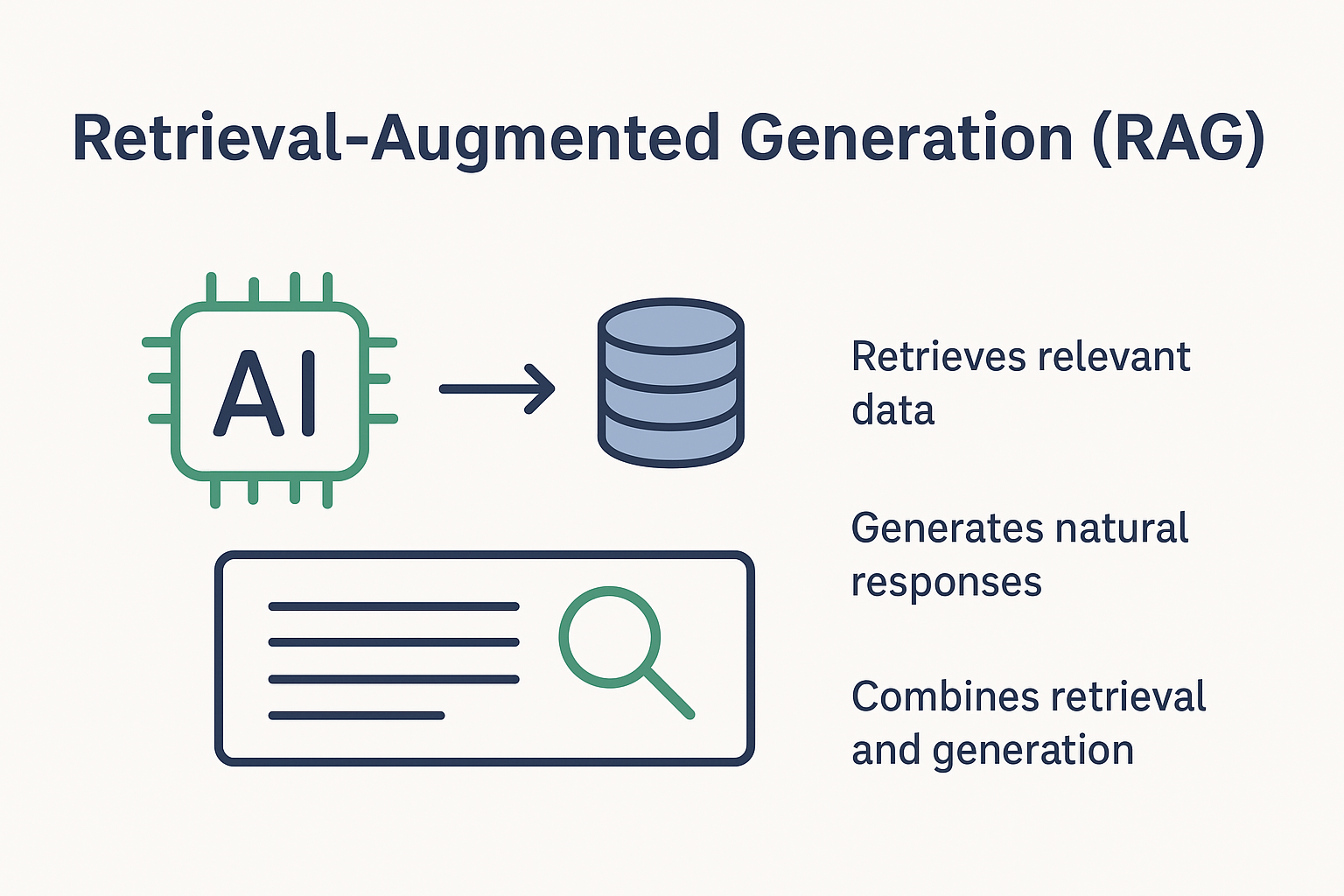
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI technique that combines information retrieval with text generation.
In simple terms:
- The system retrieves relevant data from a knowledge base
- That data is added as context
- The LLM generates a grounded response
Unlike traditional LLMs, RAG does not rely only on training data. This makes RAG in AI far more reliable for real-world applications.
Why RAG Is Needed in Modern AI Systems
Traditional generative models have three major limitations:
1. Static Knowledge
LLMs are trained on historical data. Without RAG, they cannot access updated or domain-specific information.
2. No Access to Custom or Private Data
LLMs cannot directly read your internal documents, PDFs, or databases.
3. AI Hallucinations
When unsure, models may generate incorrect but confident answers.
RAG architecture solves all three problems by grounding responses in real, retrievable data.
RAG Architecture Explained
The RAG pipeline follows a clear and efficient flow:
1. User Query
A user asks a question, such as:
“What is the role of vector databases in AI?”
2. Query Embedding
The query is converted into vector embeddings that capture semantic meaning.
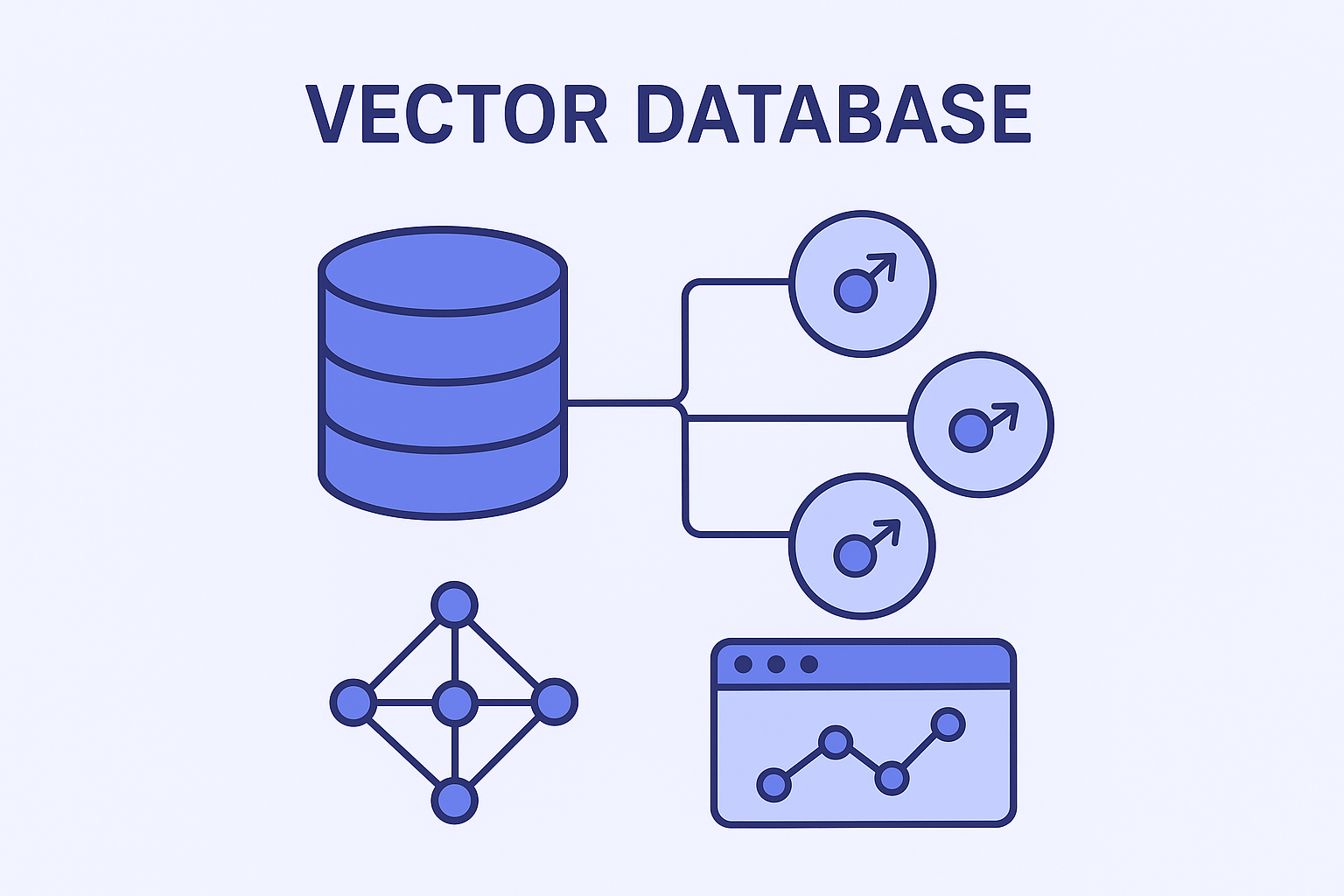
3. Vector Database for RAG
A vector database (such as FAISS, Pinecone, or Weaviate) stores embeddings of documents, blogs, and knowledge sources.
The system performs semantic search to find the most relevant content.
4. Retriever
The retriever selects the top-matching documents, ranking them by relevance.
5. Context Augmentation
The retrieved content is injected into the prompt, creating a context-aware input for the model.
6. LLM Generation
The LLM with external data generates a response using both:
- The user query
- The retrieved knowledge
This greatly reduces hallucinations and improves accuracy.
Why RAG Is Better Than Fine-Tuning
Many teams compare RAG vs fine-tuning when building AI applications.
RAG advantages:
- No need to retrain models
- Faster updates when data changes
- Lower cost
- Better explainability
Fine-tuning works well for behavior changes, but RAG is ideal for knowledge-driven applications.
RAG Use Cases in Real-World Applications
RAG is widely used across industries:
- RAG chatbots for customer support
- Enterprise AI knowledge assistants
- Document Q&A AI for PDFs and reports
- AI-powered search platforms
- Context-aware AI for internal tools
- Semantic search AI systems
Any application that needs accurate answers from custom data can benefit from RAG.
Benefits of Using RAG in AI Applications
- ✅ Reduces AI hallucinations
- ✅ Improves answer accuracy
- ✅ Uses private and dynamic data
- ✅ Scales easily with growing knowledge
- ✅ Cost-effective compared to fine-tuning
This makes RAG LLM architectures a preferred choice for production systems.
When Should You Use RAG?
You should use Retrieval-Augmented Generation if:
- Your data changes frequently
- You need explainable and reliable answers
- Accuracy is more important than creativity
- You are building enterprise-grade AI solutions
Conclusion
Retrieval-Augmented Generation is transforming how AI systems access and use knowledge. By combining retrieval, vector databases, and generative AI, RAG creates intelligent systems that are accurate, trustworthy, and practical.
As generative AI continues to evolve, RAG architecture is becoming the foundation of real-world AI applications.