If you follow the world of AI — or even casually hear about ChatGPT, BERT, or Whisper — you’ve already touched the impact of Transformers. They’re not just another neural network architecture; they’re the reason modern AI feels powerful, smart, and almost magical.
In this blog post, let’s break down what transformers are, why they changed the game, how they work, and where you’ll find them today — in simple, human-friendly language.
Overview
Transformers were introduced in 2017 in a landmark research paper titled “Attention Is All You Need.”
Before that, most AI systems relied on RNNs and LSTMs to understand sequences like text and speech. These older architectures worked — but they were slow, struggled with long context, and were hard to scale.
Transformers completely reimagined how machines process information. Instead of reading data step-by-step (like RNNs/LSTMs), transformers look at all the data at once and figure out what matters most. This unlocked a new era of large-scale AI models and led to breakthroughs across text, images, audio, and more.
What Are Transformers?
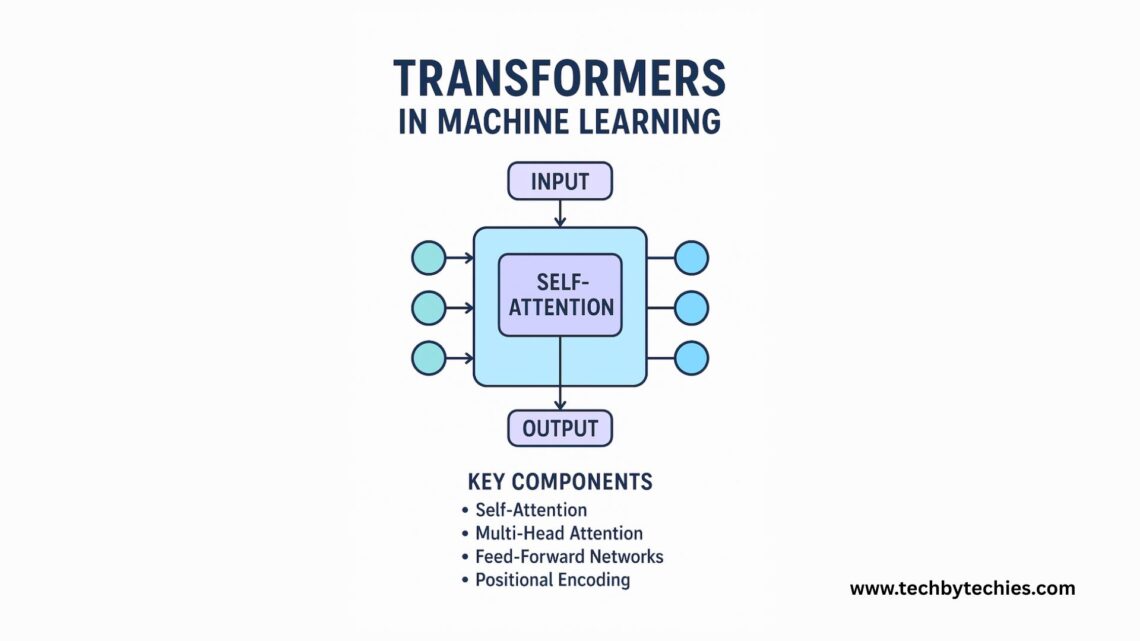
A transformer is a type of deep learning architecture designed to understand sequences using a mechanism called self-attention.
Think of self-attention as giving a model the ability to “focus” on the most important parts of a sentence or input — almost like how humans pay attention to certain words or cues when reading.
For example, in the sentence:
“The cat sat on the mat because it was tired.”
To understand what “it” refers to, the model needs to connect “it” to “cat.” Transformers are great at making these long-distance connections.
Unlike older models, transformers:
- Don’t need to read text word-by-word
- Process everything in parallel
- Understand relationships more deeply
This makes them extremely fast and incredibly accurate.
Why Are Transformers So Powerful?
Transformers became popular because they combine speed, scalability, and contextual understanding in a way older models couldn’t.
Here’s what makes them stand out:
1. They handle long sequences really well
RNNs forget relationships as sentences grow longer. Transformers don’t.
2. They process data in parallel
This massively speeds up training — especially on GPUs/TPUs.
3. They scale beautifully
The bigger the model and data, the better the performance. This is why GPT-4, Claude, and LLaMA exist.
4. They work for every type of data
Originally built for text, transformers now power:
- Image recognition
- Speech-to-text
- Audio generation
- Code generation
- Multimodal models
They’ve become the backbone of modern AI.
Key Components of a Transformer
Even though transformers sound complex, their building blocks are surprisingly elegant:
1. Self-Attention
This mechanism lets the model understand how each part of the input relates to every other part.
2. Multi-Head Attention
Instead of one single attention mechanism, transformers run many in parallel. Different “heads” capture different patterns.
3. Feed-Forward Networks
After attention figures out relationships, these layers process the information further.
4. Positional Encoding
Since transformers don’t read sequentially, they need special “position signals” to understand word order.
5. Encoder–Decoder Structure (optional)
- Encoders: Best for understanding text (e.g., BERT)
- Decoders: Best for generating text (e.g., GPT)
- Encoder–Decoder combo: Great for translation tasks
Examples of Popular Transformer Models
Transformers are everywhere. Here are some of the most important ones:
1. BERT (2018)
BERT stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers.
It reads text in both directions (left→right and right→left) and develops a rich understanding of context.
Used for:
- Search engines
- Text classification
- Sentiment analysis
- Question answering
2. GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
GPT models use the decoder part of transformers to generate text.
They complete sentences, answer questions, write code, and even create stories.
Used for:
- Chatbots
- AI assistants
- Code generation
- Content creation
3. Vision Transformer (ViT)
Transformers aren’t just for text. ViT applies the same idea to image patches, treating images like sequences.
Used for:
- Image classification
- Medical analysis
- Computer vision research
4. T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer)
T5 reframes every NLP task as a text-to-text problem.
Translation, summarization, classification — everything becomes “input text → output text.”
5. Whisper
OpenAI’s speech recognition model based on transformers.
Used for:
- Transcribing audio
- Translating speech
- Multilingual ASR tasks
Transformers have become a universal solution for almost any AI problem.
How Do Transformers Differ from RNNs/LSTMs?
Before transformers, we relied heavily on RNNs and LSTMs for sequence tasks. Here’s the difference:
| Feature | RNN/LSTM | Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Step-by-step (slow) | Parallel (fast) |
| Long context | Weak | Excellent |
| Scalability | Hard | Extremely scalable |
| Training speed | Slow | Very fast |
| Memory of past tokens | Limited | Global |
| Uses | Basic NLP tasks | Modern AI, LLMs, vision, audio |
Transformers didn’t just beat RNNs — they replaced them almost entirely.
How Transformers Power the Technology We Use Every Day
TTransformers power most of the AI technologies we use every single day — often without us even realizing it. From the apps we scroll to the tools we create with, transformers are working quietly in the background to make everything smarter, faster, and more accurate.
Here are some familiar places where transformers show up:
- Google Search → BERT
Helps understand your search queries and deliver accurate results. - ChatGPT → GPT
Generates human-like text, answers questions, writes code, and more. - Photoshop AI Tools → Vision Transformers (ViT)
Improve image editing, object detection, and smart selection features. - YouTube Subtitles → Whisper
Transcribes speech to text and handles multilingual audio. - GitHub Copilot → Code Transformers
Assists developers by predicting code and completing functions.
If you’re streaming a video, chatting with an AI assistant, or simply searching the web — transformers are already working for you in the background.
Conclusion
Transformers aren’t just another machine learning idea — they’re the foundation of today’s AI revolution.
They’re fast, powerful, scalable, and incredibly flexible. From language to images to audio, transformers continue to push the boundaries of what AI can do.
If you’re building modern AI systems, understanding transformers isn’t optional — it’s essential.