Learn what vector databases are, why traditional databases fall short, and how vector databases power modern AI applications like chatbots, semantic search, and recommendation systems.
Overview
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence has moved far beyond simple rule-based systems. Modern AI applications aim to understand meaning, context, and similarity, not just exact values. However, traditional databases were never designed for this kind of intelligence.
This is where vector databases have emerged as a game-changer.
As data grows not only in volume but also in complexity, traditional databases are increasingly challenged to support modern AI-driven use cases. Applications such as semantic search, recommendation engines, image recognition, chatbots, and large language models (LLMs) rely on understanding meaning rather than exact matches. This is where vector databases come into play.
In this blog, we’ll explore:
- Limitations of existing RDBMS and NoSQL databases
- What a vector database is
- Why vector databases are needed
- How vector databases power AI applications
- Popular vector databases available today
Problems with Existing Databases (RDBMS & NoSQL)
Before understanding why vector databases are important, let’s look at why existing databases struggle with AI workloads.
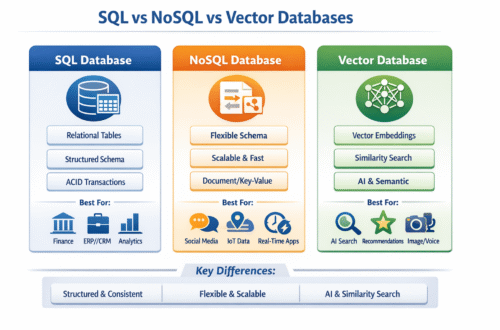
Limitations of RDBMS
Relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server are excellent for structured, transactional data. They work perfectly when you know exactly what you’re searching for.
But AI systems don’t work that way.
Key challenges with RDBMS:
- Built for exact matches, not similarity or meaning
- Not suitable for storing high-dimensional vectors (hundreds or thousands of numbers)
- Poor performance when calculating similarity metrics like cosine or Euclidean distance
- Rigid schemas make it difficult to evolve AI models
Limitations of NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases such as MongoDB, Cassandra, and DynamoDB offer flexibility and scalability, but they still fall short for semantic and AI-driven search.
Common limitations:
- Optimized for key-value or document lookups, not similarity search
- No native support for efficient nearest neighbor search
- Indexes are not designed for embeddings
- Requires complex custom logic for AI use cases
👉 Bottom line: Traditional databases are great for storing data, but not for understanding it.
What Is a Vector Database?
A vector database is a specialized database built specifically to store, index, and search vector embeddings efficiently.
What are vector embeddings?
Vector embeddings are numerical representations of data created by machine learning models. They capture the meaning of data rather than just its surface form.
Examples:
- Text → sentence or document embeddings
- Images → visual feature embeddings
- Audio → sound or speech embeddings
Each item is represented as a point in a high-dimensional space, where similar items are placed closer together.
What makes vector databases different?
Vector databases are designed to:
- Store millions or billions of high-dimensional vectors
- Perform ultra-fast similarity searches
- Support distance metrics such as:
- Cosine similarity
- Euclidean distance
- Dot product
Why Do We Need Vector Databases?
Traditional databases answer questions like:
“Find records where value equals X.”
Vector databases answer more human-like questions:
“Find items that are most similar to this.”
Why this matters
Modern AI applications rely heavily on similarity rather than exact matching.
Key benefits of vector databases:
- Semantic understanding instead of keyword matching
- Extremely fast similarity search using optimized indexing algorithms (HNSW, IVF, PQ)
- Scales efficiently for large AI workloads
- Enables real-time AI experiences
Use Cases of Vector Databases
Vector databases are already powering many AI-driven products we use every day.
1. Semantic Search
Search results based on meaning, not just keywords. For example, searching “best budget phone” returns relevant results even if those exact words aren’t present.
2. Recommendation Systems
Used by e-commerce, streaming platforms, and news apps to recommend products, movies, or articles based on user behavior and similarity.
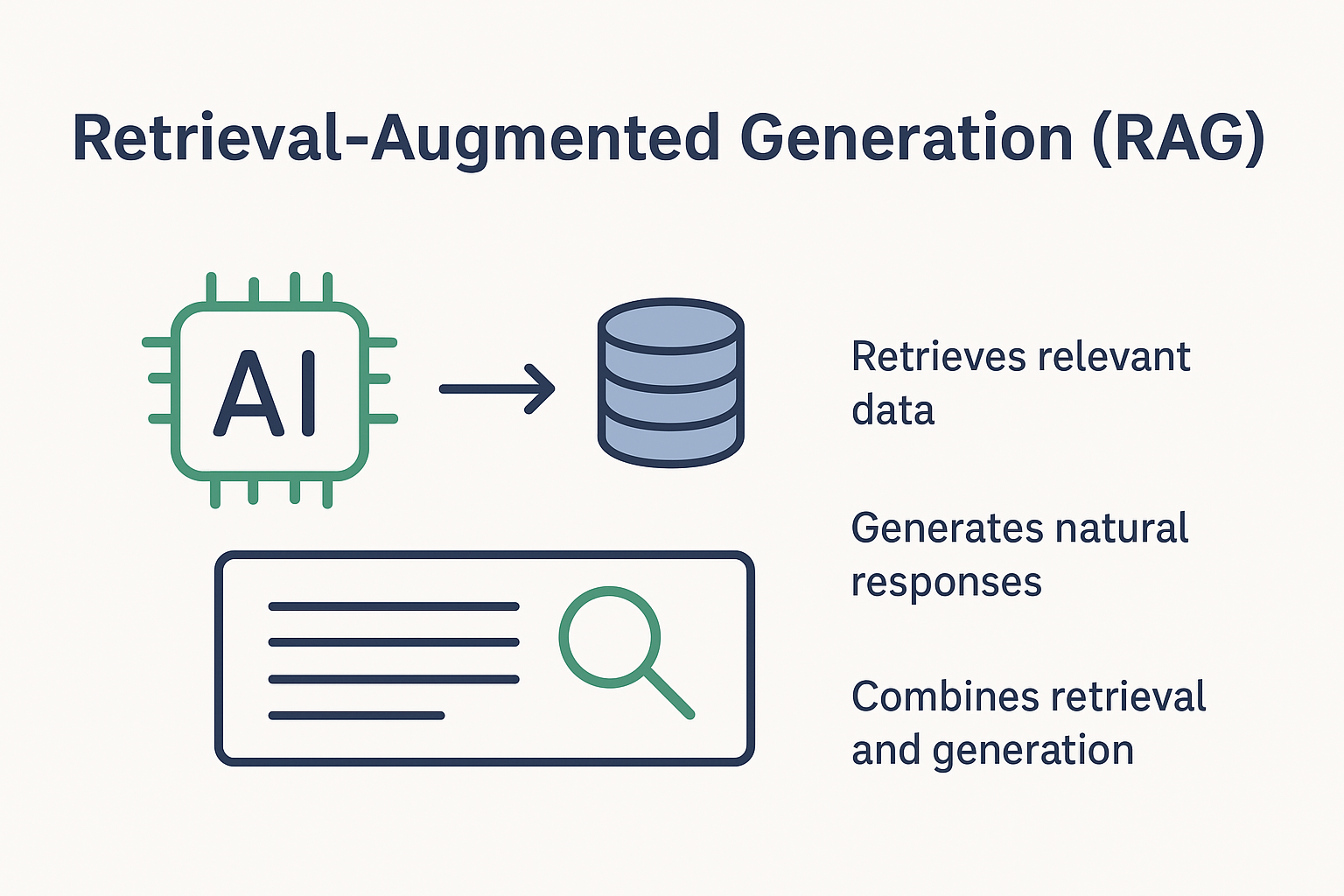
3. Chatbots & LLM Applications (RAG)
Vector databases retrieve relevant context that Large Language Models use to generate accurate and grounded responses.
4. Image and Video Search
Find visually similar images or videos instead of relying on tags or metadata.
5. Fraud and Anomaly Detection
Detect unusual behavior by comparing patterns in vector space.
How Vector Databases Power AI Applications
Vector databases play a central role in modern AI architecture.
A typical AI workflow looks like this:
- Raw data (text, images, audio) is converted into embeddings using ML models
- Embeddings are stored in a vector database
- User queries are also converted into vectors
- The vector database finds the most similar results
- Retrieved data is passed to AI models for reasoning or generation
This approach is the foundation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which significantly improves accuracy and reduces hallucinations in LLMs.
Popular Vector Databases Available Today
1. Pinecone
Description: Fully managed, cloud-native vector database optimized for AI workloads.
- High performance and scalability
- Strong ecosystem for LLMs
Link: https://www.pinecone.io/
2. Milvus
Description: Open-source vector database designed for massive-scale similarity search.
- Supports billions of vectors
- Widely adopted in enterprise AI systems
Link: https://milvus.io/
3. Weaviate
Description: Open-source vector database with built-in ML integrations.
- Supports hybrid (vector + keyword) search
- GraphQL and REST APIs
Link: https://weaviate.io/
4. FAISS
Description: Facebook AI Similarity Search library for fast vector search.
- High performance
- Often embedded into custom systems
Link: https://github.com/facebookresearch/faiss
5. Chroma
Description: Lightweight, developer-friendly vector database for LLM apps.
- Ideal for prototypes and local RAG systems
Link: https://www.trychroma.com/
6. Qdrant
Description: Open-source vector database with strong filtering capabilities.
- Rust-based, high performance
- Popular for production AI systems
Link: https://qdrant.tech/
7. Elasticsearch (Vector Search)
Description: Traditional search engine extended with vector search capabilities.
- Useful for hybrid search use cases
Link: https://www.elastic.co/
Conclusion
Vector databases have become a core building block for modern AI systems. While RDBMS and NoSQL databases remain essential for transactional and structured data, they are simply not designed for semantic similarity or high-dimensional embeddings.
If you are building applications involving AI, LLMs, chatbots, recommendation engines, or semantic search, a vector database is no longer optional—it’s essential.
As AI adoption continues to grow, vector databases will play a key role in helping systems understand data the way humans do: by meaning, context, and similarity.